Glass and glass units for spider glazing systems:
 Safety above all else – the type and structure of glazing for “spider” structures should be selected taking into account the building regulations for the safe usage of buildings and the type of “spider” system envisaged by the project. Glazing must meet the following requirements:
Safety above all else – the type and structure of glazing for “spider” structures should be selected taking into account the building regulations for the safe usage of buildings and the type of “spider” system envisaged by the project. Glazing must meet the following requirements:
- ● in the event of glass breakage, it must prevent or minimize the risk of injury to people;
- ● when used in enclosing structures, exclude the possibility of a person falling;
- ● ensure the safety of visitors as well as technical staff during cleaning and maintenance of the building;
Only glass from the safe category makes it possible to fulfill these requirements. In any case, it is acceptable to only use tempered glass, whether it is single-layer monolithic or laminated glass, or glass that is part of insulating glass units.
| Linear sizes | ≤ 2 мм |
| Arch (for curved glass) | 2 мм/м |
| Diameter of opening | – 0,2 + 0,8 мм |
| Location of openings | ≤ 1,5 мм |
Since in “spider” systems the glass not only fulfills the function of filling light openings, but also is an important load-bearing structural element, the highest requirements are imposed on its manufacture. This includes edging, drilling, tempering, Heat Soak testing (which eliminates the risk of spontaneous destruction of tempered glass caused by the presence of nickel sulfide inclusions) and strict quality control at every stage of production.
“Spider” glazing systems are designed for the construction of vertical and inclined facades, roofs, domes and canopies, as well as for various interior solutions. The glass panels used are usually rectangular and can be flat or curved. Various colors and shades of glasses and coatings, and the possibility of applying colored enamels and drawings to them, provide the architect with ample opportunities to create original projects.
Types of glazing for spider systems:
Monolithic tempered glass – single glazing (10, 12, 15, 19 mm thick):
- colorless;
- extra-transparent;
- toned in bulk (bronze, gray, green, blue);
- enameled (RAL colors);
- decorated with silk-screen printing;
- glasses with hard pyrolytic sun-reflecting coatings, as well as some models of reflective glass with magnetron sputtering.
Multiple-layer laminated glass – single-chamber glazing (external – 8, 10, 12, 15, 19 mm, internal – 6, 8, 10 mm):
- all of the aforementioned types of glass with a polymer film interlayer can be used;
- when using sun-reflecting glass, the configuration, where the reflective layer comes in contact with the polymer film, must not be used;
- for lantern glazing and awnings, only glazing elements containing laminated glass are used;
- as part of a multilayer laminated glass piece, in which the outer glass is tempered, it is possible to use heat-strengthened glass as the outer layer. Due to the different nature of damage (small fragments for tempered glass and large fragments for heat-strengthened glass), the damaged glazing element can be kept in place of installation until it is replaced;
- a preliminary calculation of the maximum temperature of the polymer layer is mandatory.
Double-glazed windows (glass thickness: external – 10, 12, 15 mm, internal – 6, 8, 10, 12 mm):
- for “spider” glazing, single-chamber glass units are usually used;
- all the aforementioned types of glass can be used, as well as energy-saving glass;
- being a type of structural glazing (the edges of the glass units are exposed to solar UV radiation), “spider” systems for assembling double-glazed windows require the use of only special UV-resistant sealants.
- it is mandatory to control the maximum temperature of the polymer layer for laminated glass and sealants used in glass units.
 When choosing the type of glass for a “spider” system, along with the criteria concerning its appearance, you must consider the following:
When choosing the type of glass for a “spider” system, along with the criteria concerning its appearance, you must consider the following:
» Calculation of deflections and workload of the glass: 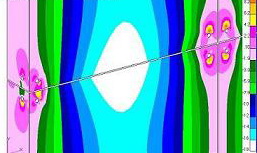 A wind load affects vertically installed elements of “spider” glazing. The weight of the glass, snow and ice loads put a strain on inclined and horizontal surfaces. These influences lead to deflection of the glass. European standards have regulations for the maximum permissible values of such deflections – no more than L / 100 for single glass and no more than L / 150 for double-glazed windows (where L is the measured side).The maximum permissible working stress on glass, measured in MPa, is also regulated. GlassPro uses the necessary analytical techniques and software to calculate the values of deflections and stresses in glass in relation to the designed object. This allows for a qualified selection of the type and structure of glazing, the thickness and dimensions of the glass elements, and to protect them and other parts of the structure from excessive deformation and damage. A wind load affects vertically installed elements of “spider” glazing. The weight of the glass, snow and ice loads put a strain on inclined and horizontal surfaces. These influences lead to deflection of the glass. European standards have regulations for the maximum permissible values of such deflections – no more than L / 100 for single glass and no more than L / 150 for double-glazed windows (where L is the measured side).The maximum permissible working stress on glass, measured in MPa, is also regulated. GlassPro uses the necessary analytical techniques and software to calculate the values of deflections and stresses in glass in relation to the designed object. This allows for a qualified selection of the type and structure of glazing, the thickness and dimensions of the glass elements, and to protect them and other parts of the structure from excessive deformation and damage. |
» Calculation of t ° of polymeric materials 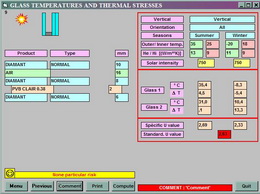 In order to ensure the safety and long-term service of the “spider” structure, a preliminary calculation of the maximum temperature of the polymer layer for laminated multi-layer glass, as well as sealants used for the assembly of insulating glass units, is mandatory. Glasspro carries out all the necessary calculations for each designed product. In order to ensure the safety and long-term service of the “spider” structure, a preliminary calculation of the maximum temperature of the polymer layer for laminated multi-layer glass, as well as sealants used for the assembly of insulating glass units, is mandatory. Glasspro carries out all the necessary calculations for each designed product. |
![]()
 TM
TM